What does anti-parallel mean in DNA. The three possible ways are.
Mode Of Dna Replication Meselson Stahl Experiment Article Khan Academy
One new strand the leading strand runs 5 to 3 towards the fork and is made continuously.

. One molecule ONLY contains new DNA. Diagram of leading and lagging replication strands. View DNA_Replication_Bozeman_Video_Guide_ from BIO 102 at Lehman College CUNY.
Mode of DNA replication. The arrow points from the 5 to the 3 end of the polynucleotide. The three steps in the process of DNA replication are initiation elongation and termination.
Molecular mechanism of DNA replication. A DNA strand is composed of a long backbone of sugar and phosphate units. B The knife-and-fork model.
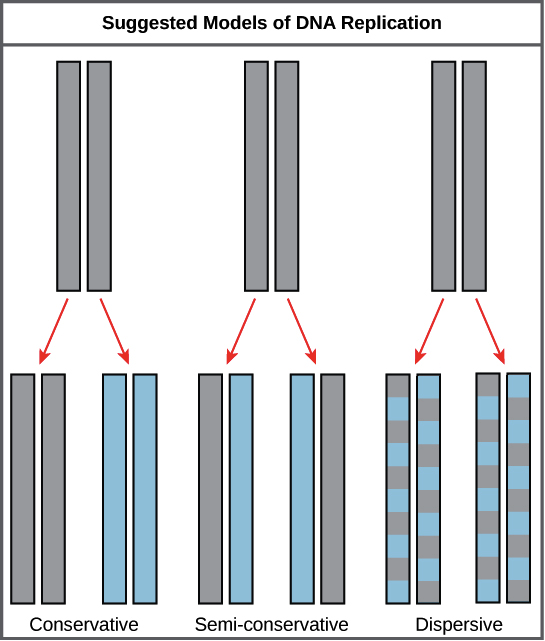
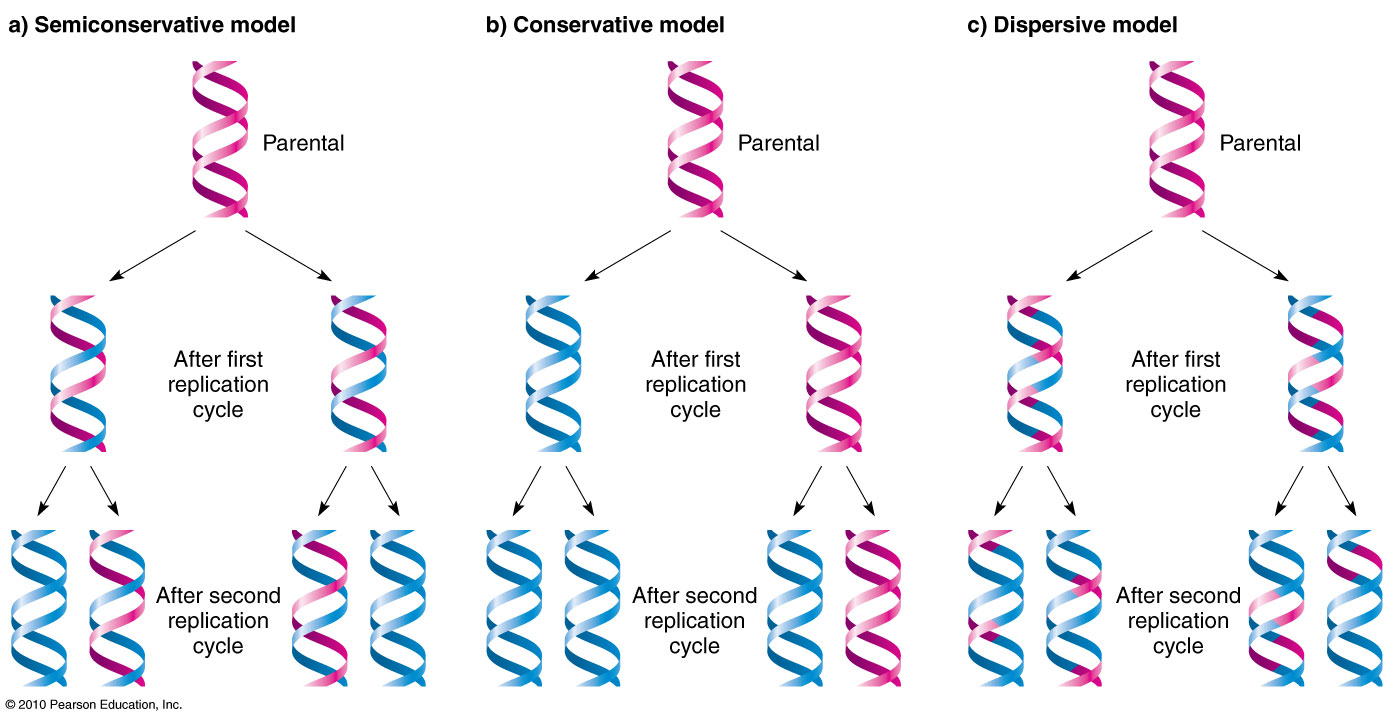
In the semi-conservative model the two parental strands separate and each makes a copy of itself. Molecular structure of DNA. Explain the 3 different theories of DNA replication.
Conservative semi-conservative and dispersive. The conservative method of replication suggests that parental DNA remains together and newly-formed daughter strands are also together. 3 DNA ligase and an enzyme that degrades RNA primers to seal together the discontinuously synthesized lagging-strand DNA fragments.
It occurs in three. However through the work of two scientist named Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl they proved that DNA replication is semiconservative. This is the currently selected item.
A THEORY OF DNA REPLICATION 489 quently joined together. Theory that says the strands of the daughter DNA molecule contain pieces of parental. 2 DNA molecules produced.
Which theory was proven to be correct. In all models the DNA that is labeled by a short period of synthesis is indicated by a thin line. 2 DNA helicases and single-strand DNA-binding SSB proteins to help in opening up the DNA helix so that it can be copied.
The invention of DNA required the appearance of enzymatic activities for both synthesis of DNA precursors retro-transcription of RNA templates and replication of singleand double-stranded DNA molecules. C The rolling circle model. See text for details.
There are three important experiments which support that DNA replication is semi-conservative. Theory that says old strands go back together. It forms the replication fork by breaking hydrogen bonds between nucleotide pairs in DNA.
There were three models suggested for DNA replication. What does 5 to 3 mean in DNA. Leading and lagging strands in DNA replication.
Primers are short RNA molecules that act as templates for the starting point of DNA replication. Explain the 3 different theories of DNA replication. After one round of replication the two daughter molecules each comprises one old and one new strand.
New strands go back together. Fragments of the original DNA molecule serve as templates for assembling 2 new molecules. DNA helicase - unwinds and separates double stranded DNA as it moves along the DNA.
The transition from the RNA to the DNA world was a major event in the history of life. It also discuss about the evidences for semi-conservative replication. Which theory was proven.
DNA replication and RNA transcription and translation. DNA Replication in Eukaryotes. There are three possible ways of DNA replication.
Lets go through Meselson and Stahl Experiment and DNA replication. D The prefork replication model. What are the basic building blocks of DNA called.
2 new DNA molecules are produced each containing one old and one new strand. This is known as semiconservative replication. Because eukaryotic genomes are very complex DNA replication is a very complicated process that involves several enzymes and other proteins.
One molecule ONLY contains old DNA. The other the lagging strand runs 5 to 3 away from the fork and is made in small pieces called Okazaki fragments. DNA primase - a type of RNA polymerase that generates RNA primers.
Describe how the Meselson and Stahl experiment proved that theory. It is because of the DNA Replication process that takes place during the S-phase synthetic phase of the cell division mitosis or meiosis in each and every cell. One of our different nucleotide bases -- A T C or G -- hang off each sugar unit.
Speed and precision of DNA replication. These include 1 DNA polymerase and DNA primase to catalyze nucleoside triphosphate polymerization. Note that after two rounds two of the DNA molecules consist only of new material while the.
DNA replication takes place in three stages. The opening of the double helix and separation of the DNA strands the priming of the template strand and the assembly of the new DNA segment. Recent data from comparative genomics structural biology and traditional.
Based on the lack of knowledge about DNA replication at the time when these 3 models were proposed any three of the DNA replication models could be correct at the time. The replication of DNA begins at a point known as the origin of replication. Explain the 3 different theories of DNA replication.
Central dogma explains how the DNA makes its own copies through DNA replication which then codes for the RNA in transcription and further RNA codes for the proteins by the translation. The sequence of the bases encodes genetic information. When two DNA copies are formed they have an identical sequence of nucleotide bases and are divided equally into two daughter cells.
DNA polymerase III reads the nucleotides on the template strand and makes a new strand by adding complementary nucleotides one after. Replication occurs in three major steps. DNA replication the process of copying DNA has three different models to explain its processes the most well-known of which is the Meselson and Stahl model.
- Semi-Conservative DNA splits in half and on each side a new DNA is formed - Conservative first DNA remains intact and makes a photocopy of itself - Dispersive chunks of DNA were being split between the two. The two DNA strands are separated by the DNA helicase. This forms the replication fork.
Three modelstheories of DNA replication. - Semi-Conservative DNA splits in half and on each side a new DNA is formed - Conservative first DNA remains intact. DNA is made differently on the two strands at a replication fork.
Semi-Conservative Conservative Dispersive models of DNA replication. 1 Dispersive 2 Conservative and 3 Semi-conservative. In molecular biology DNA replication is the primary stage of inheritance.

0 Comments